U.S. Recession in 2024?
Recessions, characterized by significant declines in economic activity across a country or region, are an inevitable part of the economic cycle. They often manifest as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth.
In this post, we’ll delve into the causes and impacts of U.S recessions and explore various indicators that could hint at an impending recession.
1. Is a Recession Looming?
The U.S. economy has been grappling with numerous challenges recently – surging unemployment claims, widespread layoffs, and rising inflation rates to name a few. The Federal Reserve has responded by hiking interest rates.
The yield on 10-year bonds is now over 5%, while the rate for 30-year mortgages exceeds 8%. These are levels unseen since the subprime mortgage-induced recession in 2007.
Given these conditions, many economists predict that another U.S recession may arrive in 2024
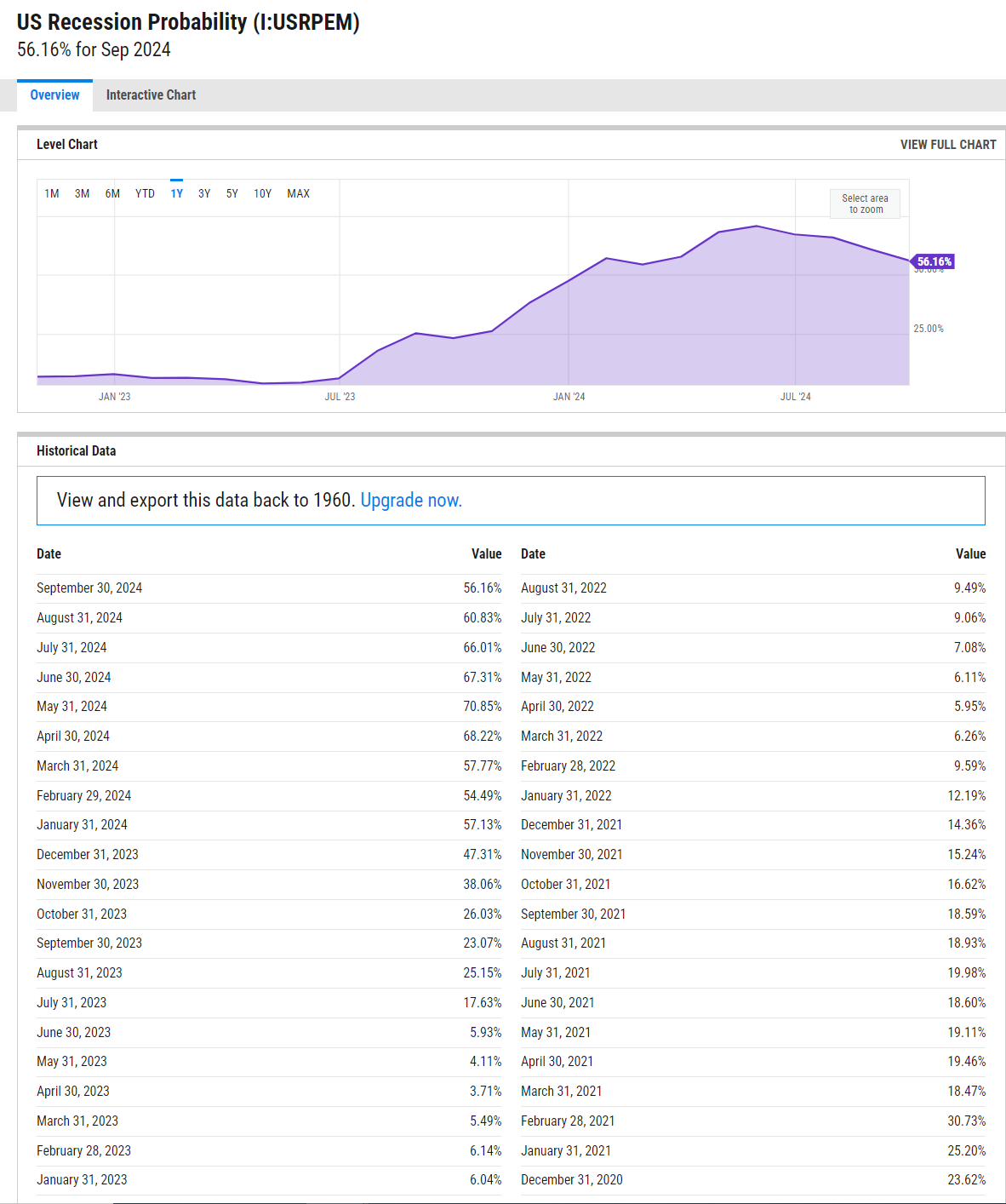 Source of Image : https://ycharts.com
Reference<1>
Source of Image : https://ycharts.com
Reference<1>
2. Economic Indices
Several indices suggest deteriorating economic conditions in the U.S., raising concerns about an impending recession.
One such measure is The Conference Board Leading Economic Index(LEI), which aggregates data from ten different indices reflecting various aspects of the U.S economy.
Currently, only one component of LEI – initial unemployment claims – indicates positive influence on the economy.
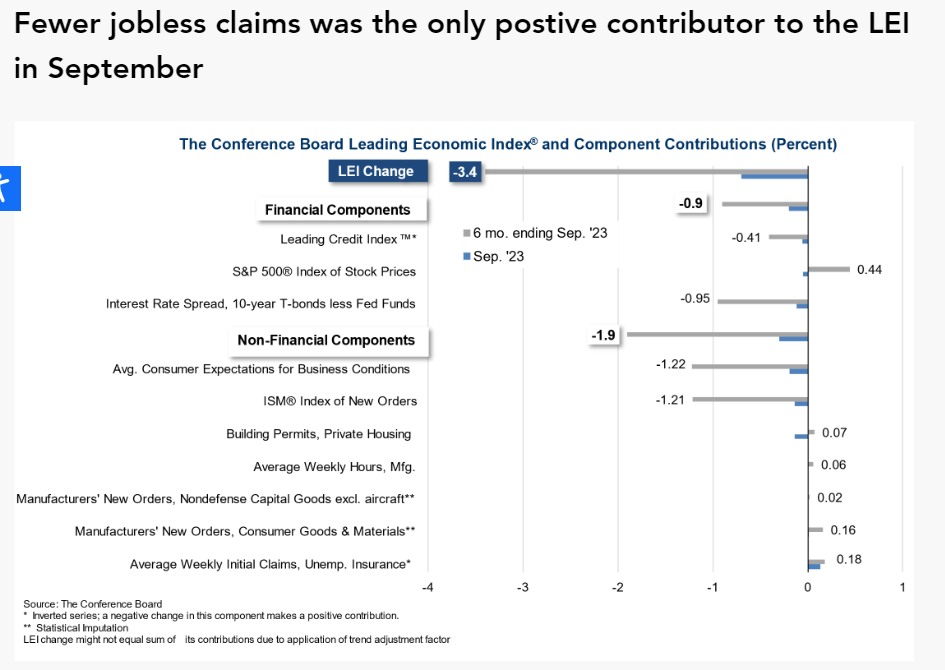 Source of Image : https://www.conference-board.org
Source of Image : https://www.conference-board.org
According to LEI’s analysis, we are currently under a “Recession signal”
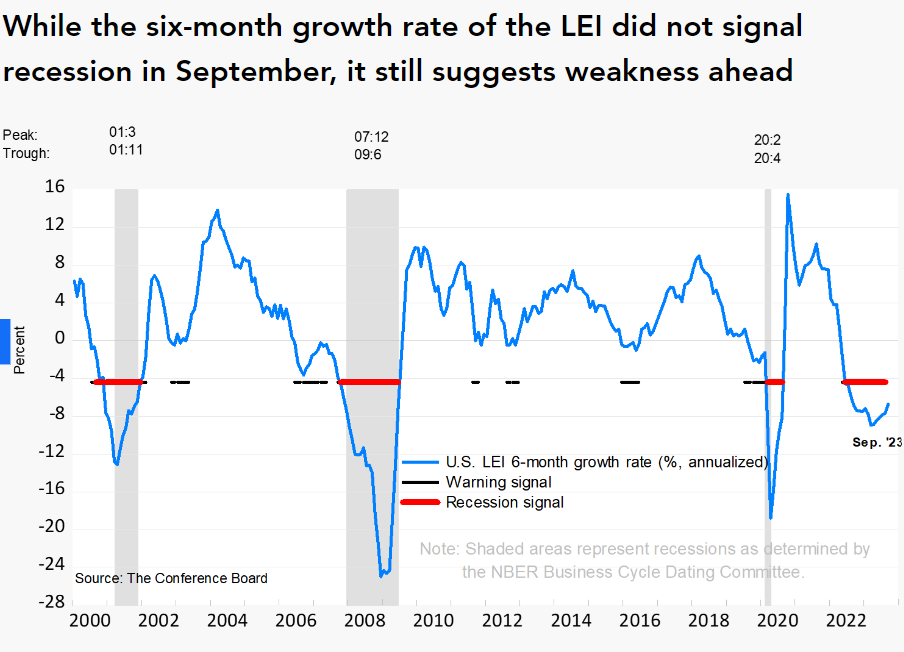 Source of Image : https://www.conference-board.org
Source of Image : https://www.conference-board.org
There are more indices that can provide valuable insights into predicting recessions. Visit my website to view these indices at a glance.
[Info] https://wegetstocksinfo.streamlit.app
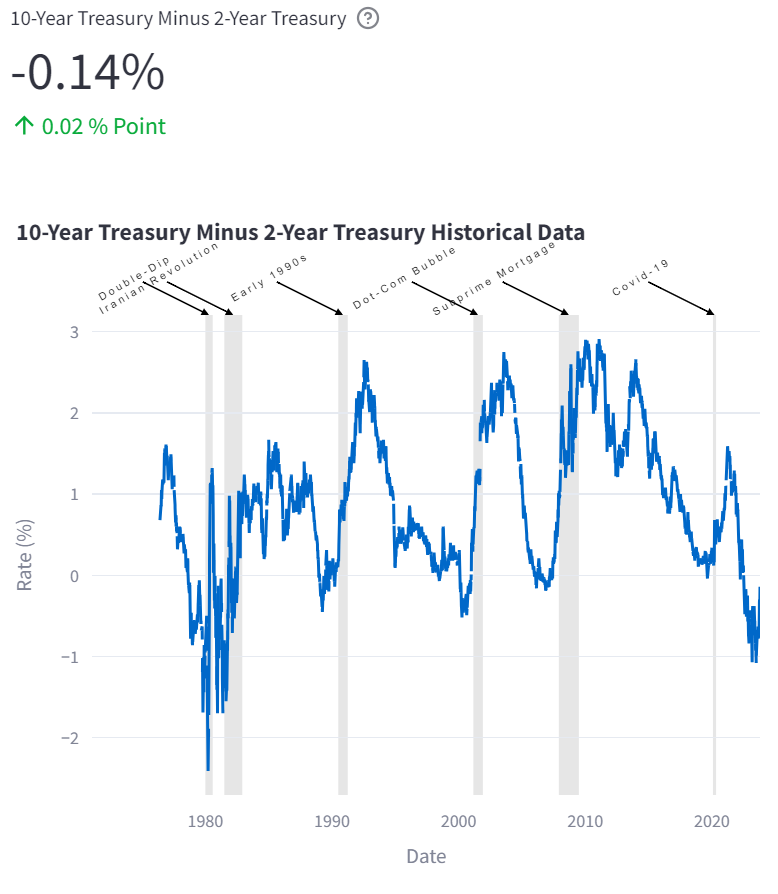
3. Yield Curve Analysis
The yield difference between long-term (10 years) and short-term (2 years) Treasury bonds is another crucial indicator to monitor when forecasting recessions.
Typically, long-term bond yields should be higher than short-term yields due to increased risks associated with time. However, this yield curve ‘inverts’ shortly before a recession – when short-term yields exceed long-term ones.
Notably, once this yield difference reverts back to positive (long-term yields being higher), history suggests that a recession could follow within six to twelve months.
In Conclusion
While predicting exact timing of recessions remains challenging due to their complex nature involving numerous factors; monitoring key indicators like those discussed can offer valuable insights into potential economic downturns.